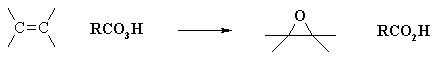تثبيت التطبيق
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
ملاحظة: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
أنت تستخدم أحد المتصفحات القديمة. قد لا يتم عرض هذا الموقع أو المواقع الأخرى بشكل صحيح.
يجب عليك ترقية متصفحك أو استخدام أحد المتصفحات البديلة.
يجب عليك ترقية متصفحك أو استخدام أحد المتصفحات البديلة.
طلب مستعجل ولايحتمل التأخير
- بادئ الموضوع بسمة
- تاريخ البدء
waleed_hamoda
Well-Known Member
waleed_hamoda
Well-Known Member
waleed_hamoda
Well-Known Member
Epoxidation

Some oxidation reactions of alkenes give cyclic ethers in which both carbons of a double bond become bonded to the same oxygen atom. These products are called epoxides or oxiranes. An important method for preparing epoxides is by reaction with peracids, RCO3H. The oxygen-oxygen bond of such peroxide derivatives is not only weak (ca. 35 kcal/mole), but in this case is polarized so that the acyloxy group is negative and the hydroxyl group is positive (recall that the acidity of water is about ten powers of ten weaker than that of a carboxylic acid). If we assume electrophilic character for the OH moiety, the following equation may be written

It is unlikely that a dipolar intermediate, as shown above, is actually formed. The epoxidation reaction is believed to occur in a single step with a transition state incorporating all of the bonding events shown in the equation. Consequently, epoxidations by peracids always have syn-stereoselectivity, and seldom give structural rearrangement. You may see the transition state by clicking the Change Equation button. Presumably the electron shifts indicated by the blue arrows induce a charge separation that is immediately neutralized by the green arrow electron shifts
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Ethers Epoxides and Thioethers[/FONT]
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Overview:[/FONT]
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Ethers Epoxides and Thioethers[/FONT][FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif][/FONT][FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]addresses the typical topics of structure, nomenclature, physical properties, preparations, reactions, and chemical analysis. A unit addressing thioethers is included.[/FONT]
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Under Nomenclature, the four important areas are addressed: common nomenclature, systematic (IUPAC), cyclic, and aromatics. These nomenclature units are designed to help students transition from one type of nomenclature to another.[/FONT]
The boiling points and solubilities of ethers stress their ability to participate in hydrogen bonding, but not generate hydrogen bonding themselves. Therefore, the low boiling points but high solubilities in water and alcohols is explained. In this section on physical properties, the ability of these ethers to form complexes as with the grignard, is used to explain their widespread use as solvents. Although crown ethers are mentioned in another unit on phase transfer catalysts, the structure is appropriately introduced in this unit.
Preparations of ethers involve dehydration of alcohols, the classic Williamson synthesis, alkoxymercuration followed by demercuration, and the formation of oxiranes. Whenever it is thought to be helpful in understanding the mechanism of these reactions, animations of mechanisms are presented.
Reactions of ethers presents the expected acid cleavage, cleavage of rings in water and alcohols, ring opening reactions as a version of acid cleavage, reactions with the grignard, and the all important section on reaction with oxygen. The dangers of ethers are often thought to lie in their flammability, and that characteristic is certainly evident. However, the ability of diethyl ether, among others, to produce “peroxides” must not be overlooked. This unit discusses how these hydroperoxides and peroxides are formed as well as simple analyses to identify their formation. The unit then suggests a few ways in which hydroperoxide and peroxide formations may be prevented.
Spectral analysis of ethers classically involves finding what is not present in the infrared. The knowledge that oxygen is present and the absence of other, characteristic oxygen signals suggests the presence of ethers. The characteristic oxonium ion formation via alpha cleavage is mentioned as possibly present in the mass spec of ethers. Downfield shifts in HNMR and CMR are also addressed.
Thioethers are presented in a separate section within this unit. Structure of thioethers, nomenclature, preparation, reactions, and characteristics are addressed. The application of the Williamson synthesis in the preparation of thioethers serves to reinforce the versatility, the limitations, and the practicality of this classic. The ability of thioethers to undergo Sn2 reactions in which they produce excellent alkylating agents is stressed for its importance in biochemistry. The unit concludes with comments regarding the general characteristics of thioethers.[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Overview:[/FONT]
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Ethers Epoxides and Thioethers[/FONT][FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif][/FONT][FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]addresses the typical topics of structure, nomenclature, physical properties, preparations, reactions, and chemical analysis. A unit addressing thioethers is included.[/FONT]
[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]Under Nomenclature, the four important areas are addressed: common nomenclature, systematic (IUPAC), cyclic, and aromatics. These nomenclature units are designed to help students transition from one type of nomenclature to another.[/FONT]
The boiling points and solubilities of ethers stress their ability to participate in hydrogen bonding, but not generate hydrogen bonding themselves. Therefore, the low boiling points but high solubilities in water and alcohols is explained. In this section on physical properties, the ability of these ethers to form complexes as with the grignard, is used to explain their widespread use as solvents. Although crown ethers are mentioned in another unit on phase transfer catalysts, the structure is appropriately introduced in this unit.
Preparations of ethers involve dehydration of alcohols, the classic Williamson synthesis, alkoxymercuration followed by demercuration, and the formation of oxiranes. Whenever it is thought to be helpful in understanding the mechanism of these reactions, animations of mechanisms are presented.
Reactions of ethers presents the expected acid cleavage, cleavage of rings in water and alcohols, ring opening reactions as a version of acid cleavage, reactions with the grignard, and the all important section on reaction with oxygen. The dangers of ethers are often thought to lie in their flammability, and that characteristic is certainly evident. However, the ability of diethyl ether, among others, to produce “peroxides” must not be overlooked. This unit discusses how these hydroperoxides and peroxides are formed as well as simple analyses to identify their formation. The unit then suggests a few ways in which hydroperoxide and peroxide formations may be prevented.
Spectral analysis of ethers classically involves finding what is not present in the infrared. The knowledge that oxygen is present and the absence of other, characteristic oxygen signals suggests the presence of ethers. The characteristic oxonium ion formation via alpha cleavage is mentioned as possibly present in the mass spec of ethers. Downfield shifts in HNMR and CMR are also addressed.
Thioethers are presented in a separate section within this unit. Structure of thioethers, nomenclature, preparation, reactions, and characteristics are addressed. The application of the Williamson synthesis in the preparation of thioethers serves to reinforce the versatility, the limitations, and the practicality of this classic. The ability of thioethers to undergo Sn2 reactions in which they produce excellent alkylating agents is stressed for its importance in biochemistry. The unit concludes with comments regarding the general characteristics of thioethers.[FONT=Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif]
[/FONT]
وبعدين عندك على الرابط التالي بعض التفاعلات
http://mihd.net/9ghpvx
وبعدين تقدري تقولي انو هما الاتنين عشان نفرق بينهم
نقدر نستخدم physical tooles
زي ال IR
وتتكلمي شويه عن ال signal for each one of them and the frequensy in which each of them apperes
http://mihd.net/yo5n9r
http://mihd.net/9ghpvx
وبعدين تقدري تقولي انو هما الاتنين عشان نفرق بينهم
نقدر نستخدم physical tooles
زي ال IR
وتتكلمي شويه عن ال signal for each one of them and the frequensy in which each of them apperes
http://mihd.net/yo5n9r
waleed_hamoda
Well-Known Member
waleed_hamoda
Well-Known Member
waleed_hamoda
Well-Known Member
mansour1973
Member
the following link may help to get better idea about eproxidation by peacids and other hydroperoxids
http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/Carey5th/Ch06/ch6-9.html
http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/Carey5th/Ch06/ch6-9.html
mansour1973
Member
sorry i realised that the same link exist already